Executive Summary Wireless connection is becoming a default option for connected everything. Cellular-IoT is becoming part of company products and…
Enterprise relationship with MNO is not always a smooth experience despite best effort of MNO and Enterprise to make this…
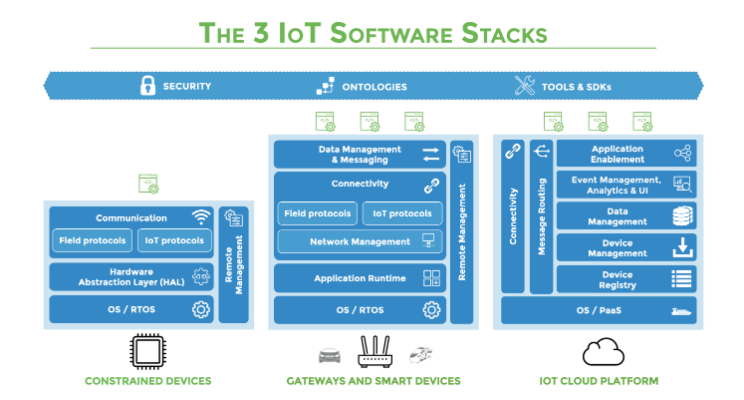
A typical IoT solution is characterized by many devices (i.e. things) that may use some form of gateway to communicate…