Executive summary Enterprise move to Mobile Platform is a necessity with wireless connection becoming a default option for connecting everything.…
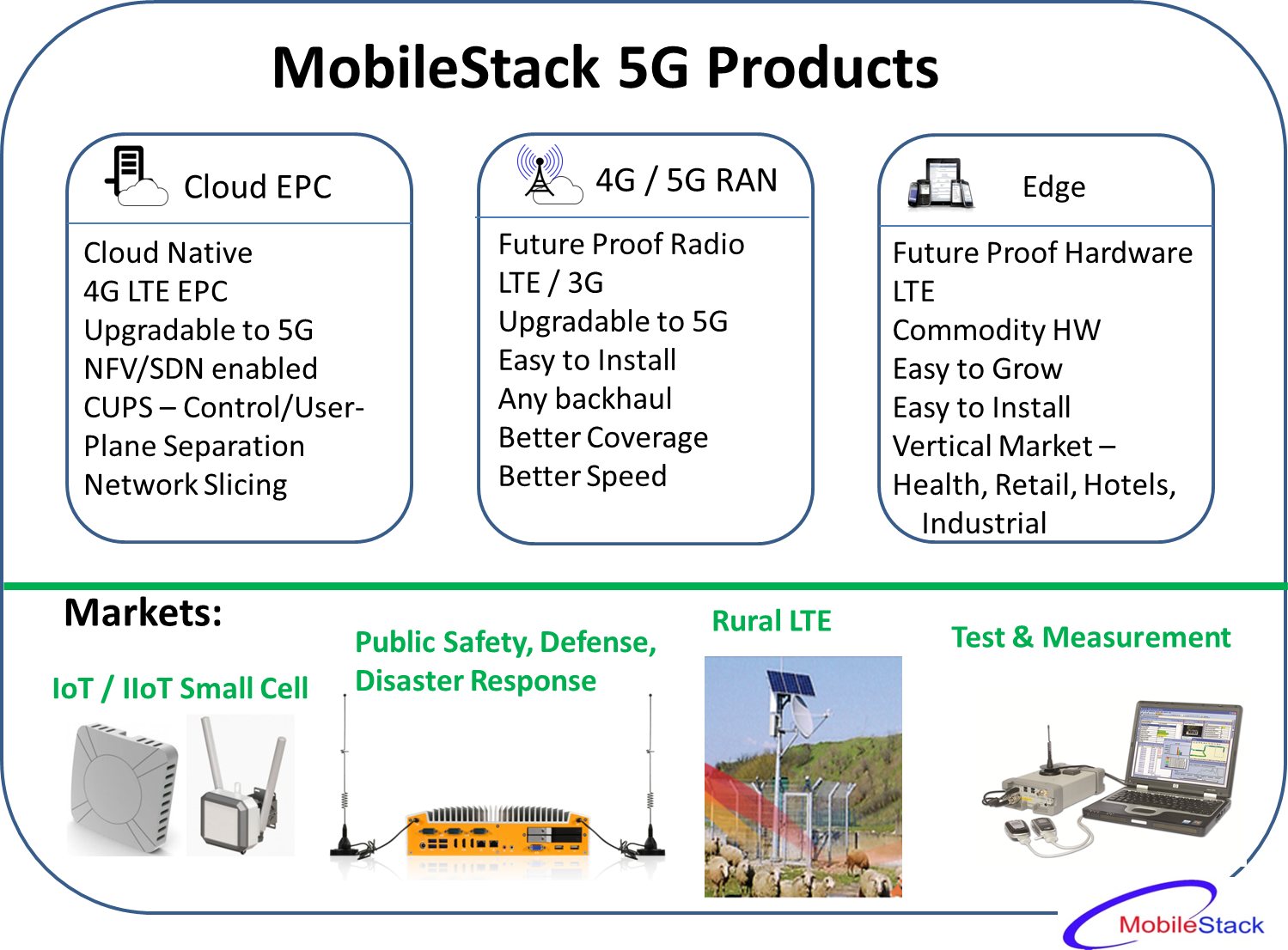
Mobilestack 5G Products using future-proof Hardware Introduction Future Proof 5G products are needed to reduce network cost with faster upgradability. …